
Pro-Russian hacktivists have escalated their activities targeting operational technology (OT) systems across critical infrastructure sectors, ushering in a new era of cybersecurity challenges. Organizations must fortify their OT security defenses as nation-state adversaries and sympathizers leverage advanced tactics to disrupt industrial operations.
This article outlines five outcome-based approaches to strengthen OT security against the increasing pro-Russia hacktivist threats plaguing the digital ecosystem in 2024.
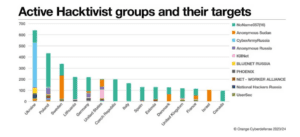
Recent Pro-Russia Hacktivist Activities
Consider the following recent hacktivist activities that made the headlines.
a. Remote Access to HMIs: In early 2024, CISA and FBI responded to U.S. water/wastewater systems (WWS) victims where pro-Russia hacktivists remotely manipulated human-machine interfaces (HMIs), disrupting operations.
According to a recent CISA Advisory report, the hackers maxed out equipment set points, disabled alarms, and changed passwords to lock out operators, causing overflows. Though disruptions were limited, the capability to inflict physical damage was demonstrated. Prompt reversion to manual controls restored operations. See:
b. Ukraine-Russia War: Check Point Research reported in 2022 that during the Ukraine-Russia war, Belarusian cyber groups opposed their government, launching attacks to hinder Russia’s troop progression. Ukraine’s IT Army mobilized, recruiting volunteers worldwide for cyber operations against Russia.
Notably, TeamOneFist targeted Khanty-Mansiysk, damaging a power plant and causing a blackout at the airport. Pro-Russian groups like Xaknet and Killnet targeted opponents, including the US, Europe, and supportive corporations.
c. Water Systems Hijack: In Q1 2024, the pro-Russian hacktivist group known as the Cyber Army of Russia claimed responsibility for launching attacks that caused a tank overflow at a Texas water treatment and processing plant – threatening to release hazardous chemicals into the water supply, according to a Field Effect report.
d. Established Bad Guys: A Hacker News report released in February 2024 named two pro-Russian hacktivist groups that impacted the private and public sectors alike in 2023 – NoName057(16) and Anonymous Sudan.
PS: You will also find Kon Briefing’s populated list of hacktivist activities and cyber attacks helpful. We urge you to check it out.
How to Strengthen OT Security Posture Against Pro-Russia Hacktivist Threats
According to Spiceworks, “The first prominent use of hacktivism in times of conflict occurred during the Kosovo War (1998-1999) when many activist groups used the Internet to denounce the aggressive measures employed by Yugoslav and NATO forces.”
Nowadays, the news is filled with reports of threat actors continuously dominating the digital landscape. How can organizations enhance their OT Security measures, improve overall security posture, and mitigate pro-Russia hacktivist threats targeting OT?
This article aims to answer these questions and achieve one objective: Harden OT security posture against pro-Russia Hacktivist threats.
Consider the following outcome-based approaches below:
1. Implement Robust Access Control and Authentication Mechanisms
Organizations must implement stringent access control measures to mitigate the risk of unauthorized access to OT systems, which could lead to system manipulation or disruption. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) must be enforced for all OT system access, including remote connections.
Biometric authentication, such as fingerprint or iris scanning, provides an additional security layer by verifying the user’s physical presence.
Source: Thibault Bougon
The principle of least privilege must be strictly adhered to, granting users only the minimum permissions required for their assigned tasks. Role-based access control (RBAC) facilitates this process by mapping user roles to specific system privileges. Regular user access reviews and prompt revocation of terminated employees’ accounts prevent unauthorized access.
2. Enhance Network Segmentation and Segregation
Effective network segmentation and segregation limit the potential spread of cyber threats within OT environments. OT networks must be isolated from corporate IT networks and the internet, creating secure demilitarized zones (DMZs) for controlled communication. Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) and firewalls segment OT networks further, isolating critical systems and limiting lateral movement in the event of a breach.
Additionally, organizations should implement unidirectional gateways or data diodes to ensure secure data transfer from OT to IT systems, preventing potential threats from propagating back into the OT network. Regular network architecture reviews and vulnerability assessments identify and address potential vulnerabilities.
3. Implement Comprehensive Monitoring and Anomaly Detection
Continuous monitoring and anomaly detection capabilities are essential for timely identifying potential cyber threats and anomalous behavior within OT environments. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) solutions and OT-specific monitoring tools provide real-time visibility into system activities, enabling rapid incident detection and response.
Machine learning and artificial intelligence establish baselines for normal system behavior and identify deviations that may indicate malicious activity. Anomaly detection algorithms analyze data sources, including network traffic patterns, system logs, and process behaviors, to detect potential cyber threats.
Furthermore, organizations must establish well-defined incident response procedures and conduct regular tabletop exercises to ensure preparedness in the event of a cyber incident. Collaboration with relevant government agencies and industry-specific Information Sharing and Analysis Centers (ISACs) facilitates intelligence sharing and coordinated response efforts.
4. Implement Robust Patch Management and Vulnerability Management
Unpatched systems and unmitigated vulnerabilities serve as entry points for pro-Russia hacktivist groups, allowing them to exploit known weaknesses and gain a foothold within OT environments. Proactive patch management and vulnerability management strategies address these security gaps.
Organizations must establish rigorous patch management processes, regularly testing and deploying security updates and patches from trusted sources. However, thorough testing in OT-specific environments is essential before deploying patches, as compatibility issues could potentially disrupt critical operations.
Vulnerability management programs must include regular vulnerability scanning, risk assessment, and prioritized remediation efforts. Compensating controls, such as virtual patching or network access controls, mitigate vulnerabilities that cannot be immediately addressed due to operational constraints.
5. Prioritize OT Security Awareness and Training
Fostering a strong security culture within the organization mitigates the risks associated with pro-Russia hacktivist threats. Regular security awareness training programs educate employees, contractors, and third-party vendors on OT security best practices, threat vectors, and incident reporting procedures.
Specialized training must be provided to OT personnel, covering topics such as secure system configuration, change management processes, and incident response protocols. Simulated phishing exercises and tabletop drills reinforce awareness and preparedness for potential cyber threats.
Organizations must establish clear communication channels and collaboration frameworks between OT and IT security teams, facilitating information sharing and coordinated response efforts in the event of a cyber incident.
Conclusion
As pro-Russia hacktivist groups continue to evolve their tactics and target critical infrastructure, organizations must adopt a proactive and comprehensive approach to OT security. Implementing robust access control, network segmentation, continuous monitoring, patch management, vulnerability management, and security awareness programs significantly enhances resilience against these threats.
Collaboration with industry partners, government agencies, and security vendors keeps organizations informed about emerging threats and facilitates the sharing of best practices. Ultimately, a multi-layered defense strategy considering both technical and human factors is essential for safeguarding OT systems and ensuring the continuity of critical operations.



