
Lalit Ahluwalia is committed to redefining the future of cybersecurity by helping large, medium, and small-scale businesses build digital trust. Here, Lalit explores the often overlooked do’s and don’ts of remote work and the security risks posed to employees and organizations alike.

Remote work has become increasingly common over the past few years. With the right policies and procedures in place, remote work can offer numerous benefits for both employees and organizations. However, it also introduces potential cybersecurity risks that must be properly addressed.
Whether you’re a seasoned remote worker or just embarking on the journey of telecommuting, there are several do’s and don’ts you should keep in mind to maximize the advantages while minimizing the security risks of this landscape.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the concept of remote work, discuss the associated cybersecurity risks, and provide you with actionable tips to minimize the security risks and safeguard your digital presence.
The Rise of Remote Work
Remote work refers to work arrangements where employees are not present on-site at a traditional workplace. Instead, they leverage technology to collaborate and complete work offsite. There are several forms of remote work, including telecommuting, virtual teams, distributed teams, and more.
Remote work offers many potential benefits, which helps explain its rising popularity. A recent Forbes report reveals that “As of 2023, 12.7% of full-time employees work from home, while 28.2% work a hybrid model.” As for what the future holds for remote work, Forbes further adds, “ According to Upwork, by 2025, an estimated 32.6 million Americans will be working remotely, which equates to about 22% of the workforce.” For employees, remote work can provide greater flexibility, improved work-life balance, avoidance of commutes, and higher productivity. Organizations can benefit through access to a wider talent pool, reduced facility costs, and higher employee retention.
With the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, many businesses were forced to rapidly implement remote work. The already growing remote work trend was dramatically accelerated. Surveys show both employers and employees want remote and hybrid work options to continue even after the pandemic subsides. As revealed by a Techopedia survey, “The prevalence of working from home was highest in the tech, finance, and professional & business services sectors.”
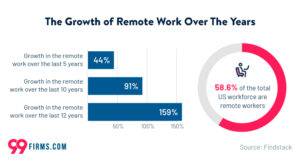 Source: 99Firms
Source: 99Firms
Cybersecurity Challenges of Remote Work
However, the remote work revolution also introduces cybersecurity challenges. When employees access and manage sensitive company data from home networks and devices, it can create cyber risks related to data protection, digital privacy, and digital trust.
Some of the core cybersecurity risks of remote work include:
- Increased phishing attacks and social engineering aimed at remote workers
- Use of unsecured home WiFi networks, which are prone to hacking
- Lack of security controls and policies for remote devices
- Unsecured handling and sharing of sensitive company data
- Limited visibility into how remote employees access data and systems
- Difficulty restricting access to authorized users and preventing credential misuse
Organizations must take steps to mitigate these risks when implementing remote work policies. Fortunately, with the right cybersecurity dos and don’ts, you can allow remote work while still protecting your data and systems.
According to a recent Research Gate paper, “Research conclusions reflect that the approach of companies and organizations to cyber risk management, providing a form of remote work organization is tailored to the industry, the nature of the information processed, the computer skills of employees, and pre-COVID-19 investments in corporate cybersecurity and digital transformation.”
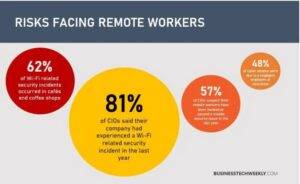
Cybersecurity Do’s of Remote Work
Here are five key cybersecurity dos to incorporate into your remote work policies and employee training:
- Require strong passwords and multi-factor authentication (MFA). Enforce password complexity and rotation policies. Enable MFA for all remote access to company systems and data. MFA adds a second layer of verification, limiting unauthorized access if a password is compromised.
- Provide a virtual private network (VPN) for remote access. A VPN encrypts internet traffic and obscures remote employee locations. VPNs with MFA provide secure encrypted access to company systems.
- Discourage the use of public WiFi. Home and public WiFi pose risks for man-in-the-middle attacks, spoofing, and snooping. A VPN can mitigate these if WiFi must be used. Also, warn employees to avoid accessing sensitive data over public WiFi.
- Enable and enforce device encryption. Require remote employees to use full-disk encryption on all devices handling company data. This helps prevent data exposure if devices are lost or stolen.
- Educate employees on responsible data handling. Train remote workers on company cybersecurity policies and best practices for data access, storage, sharing, and disposal when working remotely. Emphasize how to identify and resist social engineering.
Cybersecurity Don’ts of Remote Work
It’s equally important to avoid these five common remote work cybersecurity mistakes:
- Don’t allow the use of personal email for company business. Personal accounts lack security controls and introduce compliance risks. Require employees to only use approved corporate email for business functions.
- Don’t let employees reuse personal passwords for work accounts. If personal accounts are compromised, it can expose corporate systems if employees use the same password everywhere.
- Don’t rely on basic antivirus protection alone. Antivirus software is useful but insufficient for securing remote work. You need a multilayered security approach.
- Don’t neglect software updates and patches. When devices aren’t regularly updated, they become vulnerable to exploits. Enable automatic updates wherever possible and notify employees of critical updates.
- Don’t assume remote employees know security protocols. Beyond policies, provide regular cybersecurity awareness training for remote staff on your security tools, safe practices, and how to identify risks like phishing.
Optimizing Remote Work Cybersecurity
By combining strong technical controls like VPNs and MFA with robust cybersecurity policies and ongoing employee education, you can maximize the productivity benefits of remote work while minimizing the risks.
It’s also important to assess your data protection and incident response plans in light of expanded remote work. Know what data and systems remote workers access, and update plans to enable remote incident response if a cyberattack does occur.
With proper precautions, your organization can adopt modern remote and hybrid work models to attract talent and improve operations without sacrificing cybersecurity. Just remember to implement key security dos while steering clear of common remote work cybersecurity don’ts. Taking a proactive approach allows your workforce to be productive and collaborative wherever they are located.
 "Digital trust" cybersecurity solutions enabling automated, real-time risk mitigation are crucial for protecting organizations in today's threat landscape.
"Digital trust" cybersecurity solutions enabling automated, real-time risk mitigation are crucial for protecting organizations in today's threat landscape.