Welcome to Cyber Watch series for today, January 12, 2024. At DigitalXForce, our Cyber Intelligence team curates a list of the latest cybersecurity news to keep you informed of stories that matter every week.

This week’s Cyber Watch top 10 list is a compilation of stories from 50+ relevant news sources across the web – all ranked according to the risk impact. We encourage you to review these stories and take steps to protect your organization. Click on each headline to read the full story.
Fallon Ambulance Attack Exposes Medical Records of 900,000+ Patients
A ransacked trove of highly sensitive patient data has been traced back to the archived records of a Boston medical transport provider, Fallon Ambulance, that ceased operations last year. Cybersecurity investigators revealed hackers spent almost two months illegally rummaging through Fallon Ambulance’s digitized files earlier this year.
The notorious extortionist hacker gang BlackCat eventually claimed credit for looting over a terabyte of confidential data abandoned in Fallon’s servers. Health Security reports, “The files contained names, addresses, Social Security numbers, COVID-19 testing and vaccination information, medical information, and information provided to Fallon in connection with employment. Fallon notified impacted individuals of the breach in December 2023.”
Fallon’s parent firm admitted the breach exposed extremely intimate health information of Americans who relied on the ambulance service before it folded in 2022. With such comprehensive profiles in their possession, cyber experts caution the thieves could impersonate the identities of victims or embarrass them through public release of medical documents.
The SEC Twitter/X Account “Briefly Hacked” Before ETF Approval
America’s financial watchdogs suffered embarrassment after scammers used social media trickery to temporarily seize control of the Securities and Exchange Commission’s Twitter profile yesterday. Impersonating SEC officials, the fraudsters fabricated a post announcing fictional approval for a lucrative Bitcoin financial product.
The deceitful tweet briefly pumped up cryptomarket optimism and prices before the Commission urgently declared the account compromised and corrected the record. Investigations revealed hackers likely swapped the SEC’s phone number onto a device they controlled to override Twitter’s limited login protections.
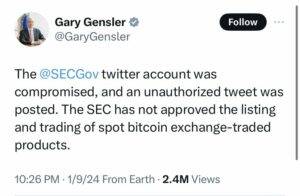
Source: Twitter/X
With no two-factor authentication activated, the SEC’s account was left wide open to impersonation despite earlier social media warnings to enable this basic security measure. The breach has provoked ridicule of the embarrassing oversight by many in the crypto community. They also called out the influence of misinformation from hacked verified profiles to manipulate digital asset prices and undermine trust.
UK’s NCSC Issues Simplified Cybersecurity Guide for Small Businesses
Britain’s cybersecurity authority has stepped in to shield smaller firms from sophisticated online attacks crippling larger counterparts. The National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) released practical guidance this week tailored to modestly-resourced businesses on guard against hackers. With limited budgets for dedicated IT security staff, the government agency hopes to make technology safety straightforward for entrepreneurs focused on daily operations rather than expert cyber defense.
The tips distill technical computer security concepts into bite-size best practices on matters like choosing secure online software services and configuring their inbuilt protections. Checking backup systems and recovery planning also feature to ensure companies can bounce back if hackers do infiltrate systems or lockdown computers for ransom.
NIST Says AI Systems Vulnerable To Tricks Causing “Spectacular Failures”
Emerging intelligent machines engineered to behave rationally can be dangerously misdirected by malicious users, warns an American government tech agency. The National Institute of Standards and Technology has briefed developers on how artificial intelligence systems are open to manipulation by crafty attacks.
By reverse-engineering queries or slipping in datasets laced with misinformation, NIST says hackers can poison decision-making algorithms to misjudge situations, violate privacy or cause accidents. With autonomous vehicles, for example, street sign sabotage could lead to catastrophic navigation errors.
NIST cautions that the vast troves of data needed to properly train complex AI make manually safeguarding against such trickery nearly impossible. While scientists grapple with theoretical solutions, they advise organizations deploying AI technologies like facial recognition or chatbots to be alert for baffling malfunctions that could signal meddling.
“China-backed Cyber Theft Threatens American AI Dominance” Warns FBI Director Wray
Washington power brokers have issued stark warnings that China is waging an intensifying espionage campaign to erase America’s technological edge in artificial intelligence research. The heads of the FBI, Christopher Wray, and the Pentagon’s Cyber Command, advised industry leaders this week that Chinese state hackers are actively infiltrating the computer networks of Google, Microsoft and other pioneering AI firms to plunder trade secrets.
With American companies currently dominating the global AI race, particularly in cutting-edge fields like self-learning software, China likely views infiltration as the fastest track to catch up on innovation. The security chiefs cautioned that stolen coding could arm adversaries with the same game-changing technology transforming cybersecurity defense tactics.
New Trend: Hackers Using Impersonation to Extort Ransomware Victims
In a disturbing trend, cybercriminals are now masquerading as ethical hackers, attempting to extort organizations hit by ransomware attacks. Arctic Wolf Labs reveals that threat actors, communicating via the secure Tox platform, pose as legitimate security researchers offering to hack into original ransomware groups’ infrastructure to delete stolen data – all for a price of five Bitcoin.
In two reported instances, the adversaries, named Ethical Side Group (ESG) and xanonymoux, falsely attribute attacks to confuse victims. Despite differences in personalities, Arctic Wolf Labs believes the same threat actor is behind the extortion attempts. The attackers claim access to exfiltrated data, demanding payment with an implied threat of future attacks if ignored. Both cases showcase a pattern: Tox communication, evidence of access to stolen data on file.io, and consistent language.
Security Lapse Exposes Sensitive Emergency Plans of Thousands of U.S. Schools, Including Active Shooter Procedures
In a significant security oversight, emergency planning documents from thousands of U.S. schools, including sensitive details on active shooter procedures, were inadvertently exposed. Discovered by security researcher Jeremiah Fowler in a 4 million-record trove linked to school software provider Raptor Technologies, the 800-gigabyte leak included evacuation plans, medical records, and threat assessments.
The exposed records, dated from 2022 to 2023, were stored in unsecured web buckets and encompassed a diverse range of emergency scenarios. Raptor Technologies, used by over 5,300 U.S. school districts, quickly secured the files after being notified by Fowler. While there’s no evidence of malicious access, the exposed information poses a potential risk if exploited by individuals with harmful intentions against schools.
CISA Issues Warning as Active Exploitation of Critical Microsoft SharePoint Server Vulnerability Raises Security Concerns
The US Cybersecurity agency, CISA, has sounded an alarm on the active exploitation of a critical Microsoft SharePoint Server vulnerability, CVE-2023-29357, with a high CVSS score of 9.8. Unauthenticated attackers can gain administrator privileges, posing a serious security threat.
The flaw, patched in June 2023, allows attackers to exploit it by sending a spoofed JSON Web Token (JWT) authentication token, requiring no user interaction for successful compromise. Discovered by Nguyễn Tiến Giang (Jang) of StarLabs SG, the vulnerability was demonstrated at ZDI’s Pwn2Own contest, earning a $100,000 prize.
Despite being classified as ‘exploitation more likely’ by Microsoft, CISA has added it to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities catalog, indicating ongoing attacks. Federal agencies must identify and patch vulnerable instances within 21 days under Binding Operational Directive 22-01, with CISA advising all organizations to promptly apply patches or discontinue vulnerable products if patches are unavailable.
WordPress Popup Builder Plugin Exploited: Balada Injector Campaign Targets Thousands with XSS Vulnerability
A critical XSS vulnerability in the widely used WordPress Popup Builder plugin has been exploited by the Balada Injector campaign. After WPScan disclosed the flaw, attackers utilized the domain specialcraftbox[.]com to inject code into over 6,200 sites, taking advantage of obfuscation techniques to hide their actions.
The injected code, triggered during the “sgpbWillOpen” event, enables attackers to execute arbitrary code. Beyond code injection, the Balada Injector operators go further, attempting to plant a backdoor for persistent access. The injected script checks admin-related cookies and, if absent, loads subsequent scripts for malicious redirects and push notification scams.
However, if admin cookies are detected, a script is executed to upload, install, and activate a malicious wp-felody.php plugin. This sophisticated attack not only highlights the importance of promptly updating plugins but also underscores attackers’ tactics of establishing a persistent presence through backdoors.
New Python-Based Hacker Tool ‘FBot’ Targets AWS, Microsoft 365, and PayPal in Active Exploitation
A potent Python-based hacking tool, FBot, has been uncovered actively targeting web servers, cloud services, and SaaS platforms, including AWS, Microsoft 365, and PayPal. SentinelOne’s researcher, Alex Delamotte, distinguishes FBot as related yet distinct from other cloud hacking tools, emphasizing its sophisticated features like credential harvesting, AWS account hijacking, and attacks against various SaaS accounts.
FBot’s objective is to hijack cloud and web services, monetizing access by selling it to other threat actors. Notable functionalities include generating AWS and Sendgrid API keys, random IP address generation, and extracting credentials from Laravel environment files. The tool exhibits active use in the wild, with samples discovered from July 2022 to the present.
While its distribution method and current maintenance status remain uncertain, signs point to FBot as a product of private development work, aligning with the trend of bespoke “private bots” tailored for individual buyers.
That’s all for today. Stay tuned for our next episode. See you next week!